PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
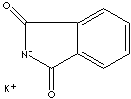
C6H4 (CO2)NHK
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
98.0% min
0.1% max
MOISTURE
0.5% max
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF IMIDE AND IMINE
|
|
|
| POTASSIUM PHTHALIMIDE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 1074-82-4 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 214-046-6 | |
| FORMULA | C6H4 (CO2)NHK | |
| MOL WT. | 185.22 | |
| H.S. CODE | 2925.19 | |
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | 1H-Isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione, potassium salt | |
| Phenylimide potassium salt 1,2-benzenedicarboximide , potassium salt 2-diazoindan-1,3-dione, potassium salt Phthalimide Potassium Salt | ||
| SMILES | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | White to light greenish powder | |
| MELTING POINT | > 300 C | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | soluble | |
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
||
| AUTOIGNITION | > 500 C | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 1 Flammability: 0 Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Moisture sensitive | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Potassium Phthalimide is used for the synthesis of N-alkylated phthalimides which produce primary amines (Gabriel synthesis) by the hydrolysis reaction. It is used as an intermediate for the synthesis of synthetic indigo, pesticides , pigments, dyes and pharmaceuticals. It is used also as a fungicide. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
greenish white powder | |
| ASSAY |
98.0% min | |
| PHTHALIMIDE |
0.1% max | |
|
MOISTURE |
0.5% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | not regulated | |
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: n/a, Risk Phrases: n/a, Safety Phrases: 24/25/28A/37/45 | ||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF IMIDE AND IMINE |
||
| Imide refers to any compound which contains the divalent radical " -C(=O)NHC(=O)-" . Imide compounds are derived from ammonia or primary amine, where two hydrogen atoms are replaced by a bivalent acid group or two monovalent acid groups, resulting in consisting of two carboxylic acid groups (or one dicarboxylic acid). In other description, Imide is a compound derived from an acid anhydride by replacing the oxygen with the =NH group. Imides are monomers to prepare polyimides that contain repeating imide groups. Aromatic polyimides have better resistance to high temperatures and corrosion than linear polyimides. Frequently, the term of imide refers to the combined forms such as maleimides, phthalimides, and succinimides which are used as plastic modifiers to improve heat-resistant, antioxidant and antifoulant properties. They are used as intermediates for the synthesis of cross-linking agents, pesticides, dyes, antiseptics and crystalline adducting agents. They are also useful compounds in the synthesis of primary amines and amino acids for the application in the field of medicine and biological research. Phthalimide, derived from phthalic anhydride with ammonium hydroxide by heating, is used in the synthesis of primary amines and amino acids. It is used to make synthetic indigo and phthalocyanine pigments which have macrocyclic structure showing striking coloring features like porphyrins (biopigments). Phthalimide has isoindole moiety. Indole structure is a motif in nature. Prominent examples include tryptophan (aromatic side chain amino acid), serotonin (neurotransmitter), auxin (plant growth hormone), and indigo (plant colorant). The radical " =NH" is called imido group. Imido is a prefix used to denote the presence in a compound of the bivalent group " =NH" attached to only acid radicals. Imine is a compound containing the bivalent " =NH" group combined with a bivalent nonacid group, as " R-HC=NH" . It is produced by the condensation reactions of aldehydes or ketones with ammonia (or amines). Imino is a prefix denoting the presence of the bivalent group " =NH" attached to nonacid radicals. | ||
|
|
|